Bed bug bites may result in raised, itchy bumps that can appear anywhere from seconds to several weeks after the bite occurs. Antihistamines and hydrocortisone creams can help reduce itching and irritation.
There are several strategies to prevent bed bug bites. Good hygiene and antihistamines are common treatment options.
This article provides a detailed exploration of bed bug bite treatment and prevention methods.
Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are small parasitic insects that feed on human blood. Although they pose a public health concern, they are not known to transmit diseases through their bites.
These pests use a small tube-like structure called a proboscis to pierce the skin and feed on blood, typically during the night or early morning when people are asleep.
It’s estimated that 1 in 5 Americans have experienced a bed bug infestation or know someone who has dealt with them.
Bite Symptoms
Most people don’t feel the bite itself but may notice small bite marks with mild irritation. Some individuals may be hypersensitive, experiencing more severe symptoms.
Itchy welts can develop a few days after the bite, though they may take up to 14 days to appear.
People may become more sensitive to bed bug bites over time, reacting faster to subsequent bites, sometimes within seconds. If left undisturbed, symptoms generally resolve within a week.
Nearly all bed bug bites cause some level of discomfort, including itchiness and inflammation. Additional signs of bed bug bites may include:
- A burning, painful sensation
- Raised, itchy bumps with a clear center
- Red or purplish bumps with a dark center and swollen surrounding area
- Small red bumps or welts in a zigzag or line pattern
- Red bumps surrounded by blisters or hives
- Papular eruptions, or inflamed patches of skin
- Small spots of dried blood on bedding or clothing
- Reddish-brown stains on fabrics from bed bug droppings
- Clear or white skins shed by maturing nymphs
The appearance of bed bug bites may vary depending on skin tone. On lighter skin, the bites often appear pink or red, while on darker skin, they may look purple and be less visible.
In rare cases, people may experience severe reactions to bed bug bites. Symptoms requiring medical attention include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Blisters
- Fever
- Nausea or flu-like symptoms
- Swollen tongue
- Irregular heartbeat
Common Bite Locations
Bed bugs can bite anywhere on the body, but they typically target areas exposed during sleep, such as:
- Neck
- Face
- Hands
- Shoulders
- Arms
- Legs
Complications
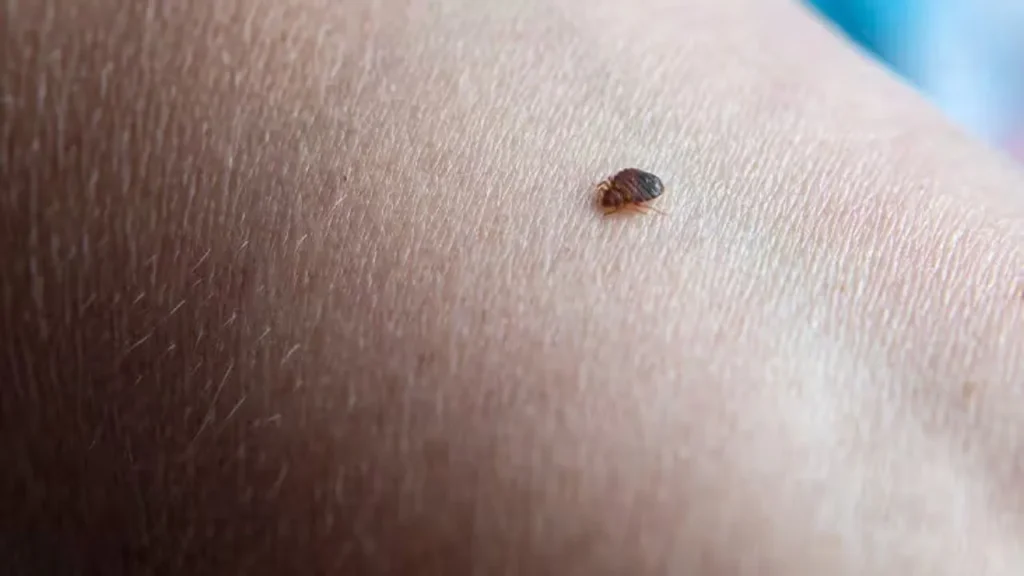

Living with bed bugs can lead to additional health issues, such as:
- Increased risk of infection: Scratching bites may damage the skin, making infection more likely.
- Sleep deprivation: Anxiety about bed bugs feeding at night can cause stress, leading to restless or disrupted sleep.
- Decreased well-being: Persistent sleep problems can contribute to depression, anxiety, fatigue, and lowered immune function. Misunderstandings about bed bugs being related to cleanliness can exacerbate these issues.
Treatment
There are limited treatment options for uncomplicated bed bug bites. The first step is to clean the wound with soap and water. Treatments to relieve minor symptoms include:
- Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream
- Anti-itch creams
- Antihistamines
Medical attention should be sought if swelling, inflammation, or itching becomes severe or persistent. A heightened immune response may indicate an allergic reaction, in which case treatments could include:
- Injectable corticosteroids
- Antihistamines
- Epinephrine medication
If infection occurs, antibiotics may be necessary. Severe itching can lead to complications like scarring, and a doctor may prescribe corticosteroid creams or antihistamine pills for relief.
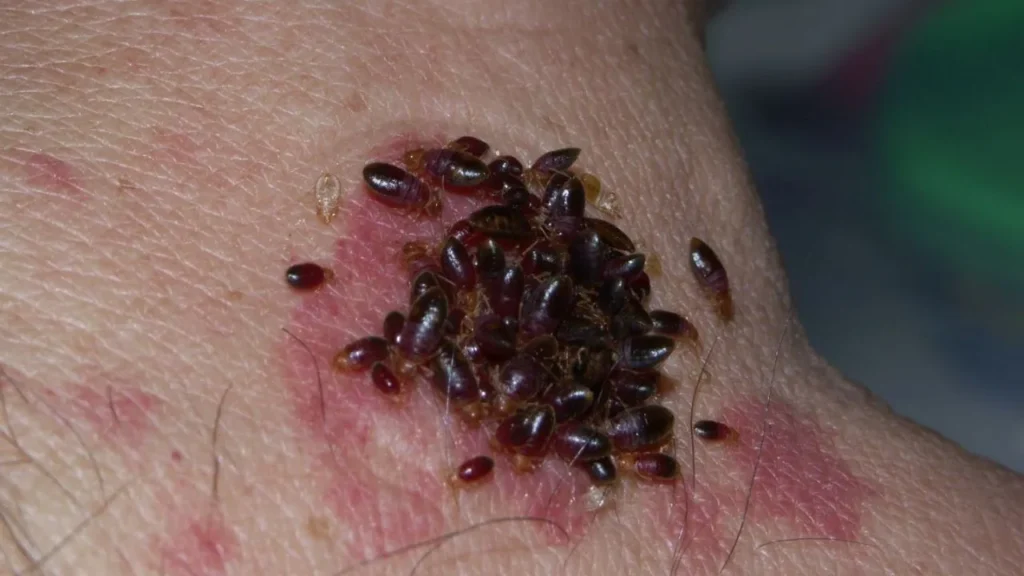
Identification of Bed Bugs
Recognizing bed bugs can help prevent exposure and infestation. Common characteristics of nymphs (young bed bugs) include:
- Less than 5 mm in length
- Whitish-yellow or clear color
- Almost invisible without magnification
Nymphs are easier to see after feeding, as their abdomen fills with blood and turns reddish-brown.
Adult bed bugs are larger and easier to spot, with the following traits:
- Oval-shaped body
- Reddish-brown to tan color
- 5–7 mm long, similar in size to an apple seed
- Flat body before feeding
- Musty or sweet odor released by glands on their underside
Bed bug eggs are small, pearl-colored, and barrel-shaped, often no bigger than the head of a pin.
Where to Find Bed Bugs
Bed bugs often hide in cracks, crevices, and seams of furniture, mattresses, walls, and flooring. They prefer to stay close to bedrooms, but finding them in other areas may indicate a larger infestation.
Common sources of bed bug spread include:
- Secondhand furniture
- New furniture or textiles exposed during transit
- Luggage
- Bedding
- Moving or storage boxes
Bed bugs do not discriminate between clean or messy environments.
ALSO READ:
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you know if a bite is from a bed bug?
Bed bug bites usually appear on exposed skin areas, such as the face, neck, and arms. Bites may leave small red dots, and blood spots or brown stains from bug droppings may be visible on bedding.
How long do bed bug bites last?
Most bed bug bites heal within a week or two.
How do you get rid of bed bug bites quickly?
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends washing bites with soap and water to prevent infection and applying a corticosteroid cream to reduce itching.
Summary
Bed bugs typically hide in bedrooms and feed on human blood during the night. Bite symptoms can take up to 14 days to appear, though they may develop sooner.
Treatments for bed bug bites include hydrocortisone, anti-itch creams, and antihistamines. If infection occurs from scratching, doctors may prescribe antibiotics.